ACL Abuse
Access Control Lists
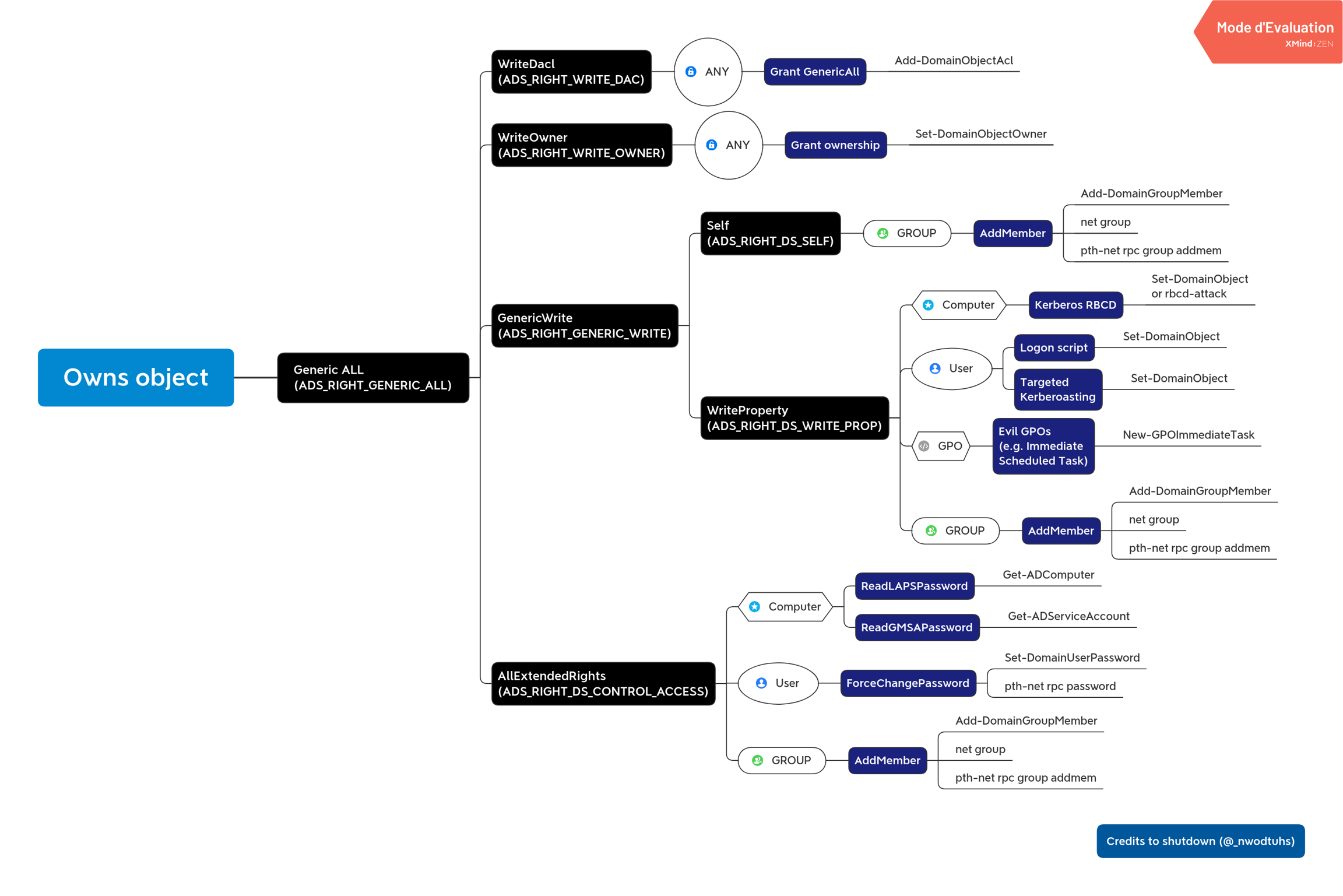
BloodHound

Some AD object security permissions abusable with PowerView / SharpView:
ForceChangePassword abused with
Set-DomainUserPasswordAddMembers abused with
Add-DomainGroupMemberGenericAll abused with
Set-DomainUserPasswordorAdd-DomainGroupMemberGenericWrite abused with
Set-DomainObjectWriteOwner abused with
Set-DomainObjectOwnerWriteDACL abused with
Add-DomainObjectACLAllExtendedRights abused with
Set-DomainUserPasswordorAdd-DomainGroupMember
ForceChangePassword
From Linux with further recovery:
SDDL
Let's say that the ACE on object A applies to object B. This grants or denies object B access to object A with the specified access rights.
ACE example in SDDL format:
Hunt for ACLs
ActiveDirectory
Enumerate ACLs which snovvcrash user possesses against j.doe user:
Enumerate which users possess GenericAll or AllExtendedRights permission against j.doe user:
PowerView analog + excluding 3-digit RIDs:
Find all users who can DCSync and convert their SIDs to names:
PowerView2
Search for interesting ACLs:
Check if the attacker "MEGACORP\sbauer" has GenericWrite permissions on the "jorden" user object:
PowerView3
Search for interesting ACLs:
Check if the attacker "MEGACORP\sbauer" (S-1-5-21-3167813660-1240564177-918740779-3102) has GenericWrite permissions on the "jorden" user object:
The -ResolveGUIDs switch shows ObjectType and InheritedObjectType properties in a human readable form (not in GUIDs).
PowerView 3.0 does not return IdentityReference property, which makes it less handy for this task (however, you may filter the output by the attacker's SID). To automatically convert SIDs to names we can use the following loop:
powerview.py
Abuse GenericAll
Find domain users that current user has GenericAll access right to:
The attacker can change password of discovered users:
Find domain groups that current user has GenericAll access right to:
The attacker can add users to discovered groups:
Enable/disable AD account remotely via ldap_shell:
Abuse WriteDACL
Find domain groups that current user has WriteDACL access right to:
The attacker can take the full control of discovered groups and then add a users to them:
Group membership will take its sweet time to be updated within target user's TGT. To force the update one may purge existing tickets and request new TGT:
Exchange Windows Permissions
Privilege escalation with ACLs in AD by example of the Exchange Windows Permissions domain group.
Add user to the Exchange Windows Permissions group:
Add DCSync Rights
Using aclpwn.py:
Using Impacket ntlmrelayx.py:
Using Impacket dacledit.py:
Using PowerView2:
Using PowerView3:
Using PowerShell ActiveDirectory:
Get ACL for the root domain object.
Get SID for the account to be given DCSync rights.
Create a new ACL and within it set "Replicating Directory Changes" (GUID
1131f6ad-9c07-11d1-f79f-00c04fc2dcd2) and "Replicating Directory Changes All" (GUID1131f6aa-9c07-11d1-f79f-00c04fc2dcd2) rights for the SID from (2).Apply changes.
Using ADSI and dsacls.exe:
Clean up:
Managed Security Groups
Returns all security groups in the current (or target) domain that have a manager set:
Enumerate the ACLs set on this group. GenericWrite privilege means that the user can modify group membership:
Tools
Aced
Last updated